R1.5 to SIP Gateway or Signaling Converter
Features
- up to 16 E1 interfaces
- up to 480 VoIP channels
- SS7, DSS1, QSIG, V5.2, R2 CAS, R 1.5
- SIP, SIP-I, RTP, RTCP, TCP, UDP
- voice codecs G.711, G.723.1, G.726, G.729a/b, GSM
- voice quality – Adaptative jitter buffer, VAD, SID, CNG
- registration and authentication – up to 5000 SIP-subscribers
- fax over G.711, T.38 fax relay
- Hardware Echo Cancellation
- Call Routing TDM-SIP, SIP-TDM, TDM-TDM and SIP-SIP
- SNMPv2 monitoring
- RADIUS login
- Security (іntegrated firewall, password protected access, SSH)
- Single/Dual-redundant 220 VAC or 48/60 VDC Input
Overview
SIP to R1.5 Gateway (R1.5 VoIP gateway) is used in different options of conjugation of VoIP and TDM/PSTN networks for minimization of expenses and reduction of operational costs. This gateway deliver reliable, high quality voice traffic between PSTN and VoIP networks.
CAS VoIP gateway due to the implementation and support of CAS type signaling is an optional product of the Terratel SIP/E1 Gateway model.
CAS or R1.5 signaling (for two dedicated signal channels) can be implemented by transmitting signals in the channels of PCM systems.
Support of all types of signallings being used on the PSTN network allows to use the equipment for reconstruction and upgrade of all types of automatic telephone exchange used on a network. Effective integration TDM to NGN and IMS networks.

Pic 1. SIP to R1.5 Gateway Connection Block Diagram.
Functionality
The device has the following important functional features:
- Supports R1.5 CAS signaling
- Up to 16 E1 and 480 SIP ports
- Supports integrated IP-PBX functions
- Simultaneously supports SS7, ISDN PRI, DSS1, QSIG, V5.2 and R2 MFC signaling within a single device
- Provides for combining several PBXs into a corporate network with internal dialing plan
- Provides for integrating IP-TDM-IP, TDM-TDM and IP-IP connections
- AC or DC backup power supply
- The possibility of reservation of communication using E1 bypass
Configuring and setting R1.5 CAS signaling
Inbound R1.5 Signaling
System R1.5 is an asymmetrical protocol that is widely used in East Europe over E1 trunks. It has provisions to interface with analog and digital switches.
Protocols R1.5 uses three different register signaling types:
- Decadic
- Multi-Frequency Pulse Shuttle (MFS)
- Multi-Frequency Continuous Packet (MFCP) (implemented specifically for the transmission of ANI information).
When organizing inbound lines over R1.5 protocol the corresponding signaling type should be selected: Inbound R1.5.
In addition to setting parameters common to all signaling types these signaling types should also have the parameters specific to R1.5 protocol set to their required values:
- Register exchange type
- CAS bits inversion.
You should also set the following additional parameters to their required values:
- Request ANI before answer
- Request ANI in answer
- Send 500Hz when ANI requested
- Request retries count
MFS set for register exchange.
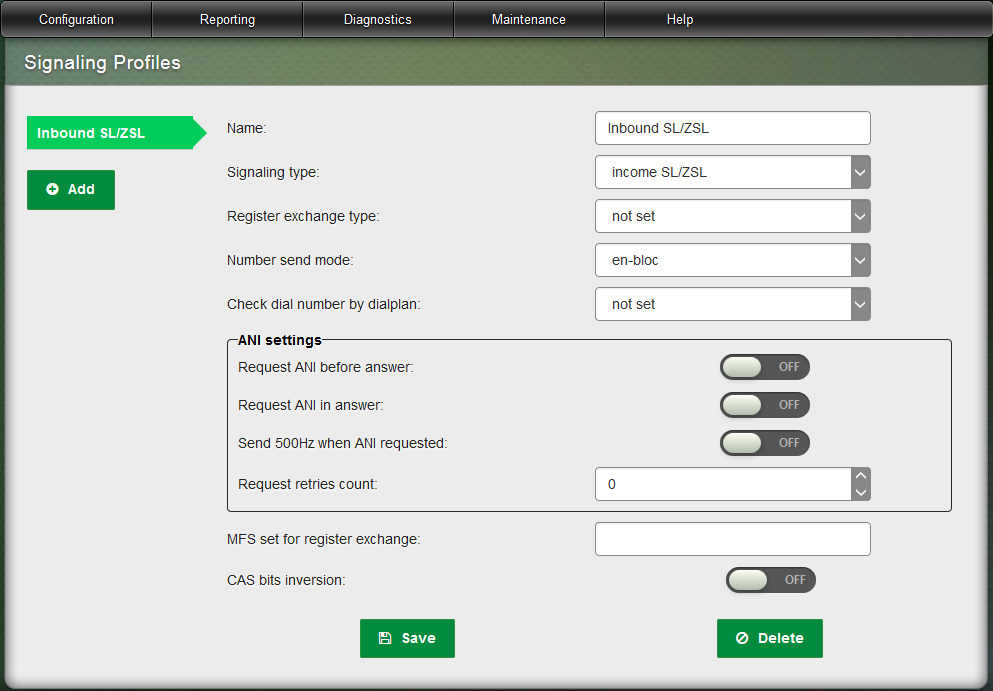
Pic 2. Web Interface – Signaling Profiles – R1.5 CAS.
Outbound R1.5 Signaling
When organizing outbound lines over R1.5 protocol the corresponding signaling type should be selected: Outbound R1.5.
In addition to setting parameters common to all signaling types these signaling types should also have the parameters specific to R1.5 protocol set to their required values:
- Register exchange type
- CAS bits inversion
You should also set the additional parameter ANI Send Condition to its required value.
Migration of PBX subscribers with R1.5 signaling to IP network
Upgrade telephone networks using R1.5 signaling, the introduction of a specialized VoIP gateway is proposed.
There are 2 options for using this gateway based on tasks to be solved.
Option 1 is used when it is required to replace digital TDM switch with the SoftSwitch. If a number of subscriber nodes are connected to the digital TDM switch via the R1.5 interface, they can be switched to the SoftSwitch soft switch using the VoIP gateway as shown in the figure.
If multiple subscriber nodes are connected to the TDM Switch over the R1.5 interface they can be switched to the SoftSwitch using the gateway as indicated on the following figure.

Pic 3. R1.5 to SIP VoIP Gateway Interconnection Diagram.
In this case the R1.5 interface disconnects from the TDM Switch and connects to the VoIP gateway that is connected to the SoftSwitch via the SIP data communications network.
Migrating SIP subscribers to PSTN via R1.5 signaling
Option 2 is used when it is required to connect VoIP subscribers from the local network to the PSTN number capacity. If the operator has the existing TDM Switch with free R1.5 interfaces the gateway on the TDM network side looks as the R1.5 subscriber node while on the IP network side it looks as the IP PBX where IP subscribers register (please see the figure).
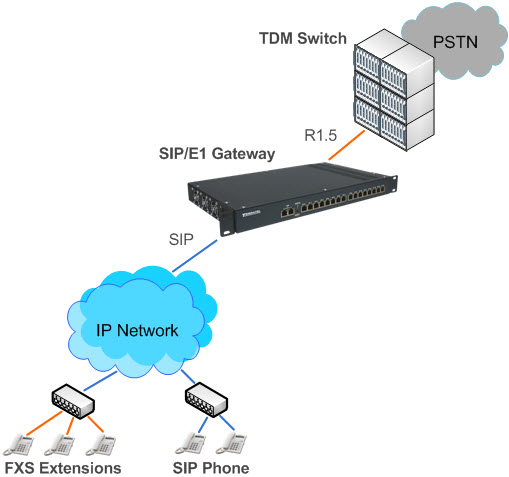
Pic 4. R1.5 VoIP Gateway to TDM switch and IP network.
The best advantage is price, because it’s less than competitors have. So the same function, but lower price – the best choice.
R1.5 (CAS) Protocol conversion option
Since the gateway supports SS7, DSS1, QSIG, V5.2 signaling it can be used as a protocol converter.
This is important when TDM networks are upgraded and it is required to adapt various telecommunications products to R1.5 interface protocols.

Pic 5. Network diagram of using the device as a signal converter R1.5 and SS7.
R1.5 СAS VoIP gateway from the company Terratel is used in different options of conjugation of VoIP and TDM/PSTN networks for minimization of expenses and reduction of operational costs.
Technical Specifications
| Network Interfaces | |
|---|---|
| TDM | up to 16 E1 interfaces |
| SIP and RTP | up to 480 VoIP channels, 10/100/1000 BASE-T Ethernet |
| Management | Fast Ethernet, RS-232 |
| Signaling Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IP | SIP, SIP-I, RTP, RTCP, TCP, UDP |
| PSTN | SS7, ISDN PRI (DSS1, QSIG, Q.931), QSIG, V5.2, R2 MFC, R2 CAS, R1.5 |
| Feature Support | |
|---|---|
| Voice codecs | G.711 (a-law, µ-law), G.723.1, G.726, G.729a/b, GSM |
| Voice processing | Adaptative programmable jitter buffer, VAD, SID, CNG |
| DTMF | RFC2833, SIP INFO, RFC 2976 |
| FAX | fax over G.711, T.38 fax relay |
| Echo Cancellation | G.168 up to 128 ms |
| Registration and Authentication | up to 10000 SIP-subscribers |
| Registration | SIP-trunks |
| Call Routing | TDM-SIP, SIP-TDM, TDM-TDM and SIP-SIP |
| Power | |
|---|---|
| Single/Dual-redundant 220 VAC or/and 48/60 VDC Input | |
| Up to 28W Power consumption (for 16 E1) |
| Operations Management | |
|---|---|
| GUI via Embedded Web Server | |
| SNMPv2 monitoring | |
| Syslog Telnet (for CLI) |
| Security | |
|---|---|
| Integrated firewall, Password protected access, SSH, RADIUS login |
| Operating Environment | |
|---|---|
| Operating temperature | from 0°С to +60°СHumidity |
| Humidity | up to 80% at +25°С |
| Hardware | |
|---|---|
| System Type | Board |
| Dimensions | 1U high, 19″ wide rack mountable |
Delivery Set
SIP/E1 Gateway Lite:
- SIP/E1 Gateway Lite (1Е1, 30 SIP channels, G.711, T38 codecs, echo cancellation G.168)
SIP/E1 Gateway:
- SIP/E1 Gateway (2Е1, 240 SIP channels, G.711, G.726, G.729, T38 codecs, echo cancellation G.168)
- SIP/E1 Gateway (4Е1, 240 SIP channels, G.711, G.726, G.729, T38 codecs, echo cancellation G.168)
- SIP/E1 Gateway (8Е1, 240 SIP channels, G.711, G.726, G.729, T38 codecs, echo cancellation G.168)
- SIP/E1 Gateway (12Е1, 240 SIP channels, G.711, G.726, G.729, T38 codecs, echo cancellation G.168)
- SIP/E1 Gateway (16Е1, 480 SIP channels, G.711, G.726, G.729, T38 codecs, echo cancellation G.168)
